Overview of AI in Search
Artificial Intelligence (AI) has been a game-changer for many industries, and search engines are no exception. AI, particularly through technologies like machine learning (ML) and large language models (LLMs), has changed how search engines work and how we interact with them. Traditional search engines relied on algorithms that ranked web pages based on keyword matches and other factors like page authority and backlinks. While these methods remain important and still have their place, the introduction of AI has allowed search engines to move beyond that, offering a more intuitive and conversational experience for users. AI in search engines does much more than simply match words to queries. It enables engines to understand the context, intent, and even the emotions behind a search. This has resulted in more relevant and useful results, even for complex or ambiguous searches.
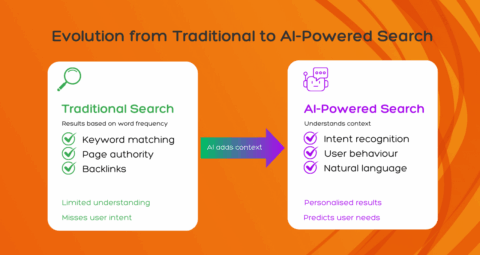
For example, if you search for “best dog breeds for small flats,” AI models can interpret the intent behind the query and generate a summary that highlights small, low-energy dog breeds that are suited to living in confined spaces, rather than just returning pages that contain the words in the search phrase.
The Role of Generative AI in Search
Generative AI is a type of artificial intelligence that can create content, including text, images, and even videos. It’s what AI Overview (AIO) is in Google for example.
In search engines, generative AI transforms the user experience by providing direct, meaningful answers to queries, often summarising information from many different sources. One of the most frequently seen applications of generative AI in search is creating short, concise answers to questions.
For instance, if you search for “how to start a small business” in Google, traditional search results would provide links to articles, blogs, and guides on the topic. Generative AI, however, could give you a summarised answer in the form of AI Overview, breaking down the steps into easy-to-follow points without requiring you to click on multiple links.
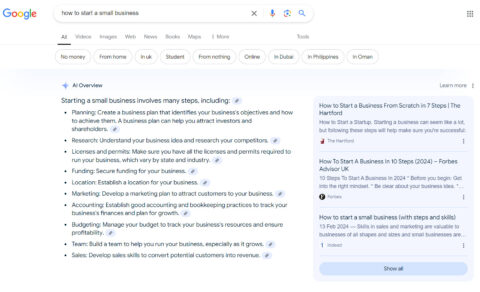
Another feature of generative AI is its ability to handle follow-up questions. After receiving an initial answer, users can ask more detailed questions, and the AI can refine its response accordingly. For example, after learning how to start a small business, a user might ask, “What are the legal requirements?” The AI can build on the original answer, tailoring it to the follow-up query.
In search engines like Google’s AI Overview, this feature reduces the time and effort users spend searching, as they no longer need to sift through multiple sources to find specific answers. However, this shift also impacts how SEO works, as the focus is no longer purely on getting users to click through to a website but on being part of the AI’s knowledge base.
What are the AI Models Powering Search?
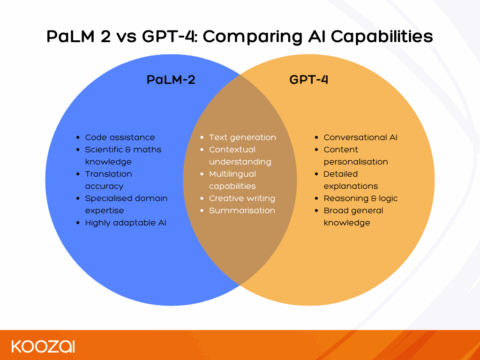
At the core of these advancements are AI models like Google’s Pathways Language Model (PaLM 2) and OpenAI’s GPT-4. These models are trained on massive datasets, allowing them to understand and generate human-like responses to complex queries.
Google’s PaLM 2
PaLM 2 is at the heart of Google’s SGE. It’s designed to handle complex queries by understanding and generating human-like text. PaLM 2 can generate highly relevant answers to diverse questions by understanding context, tone, and even nuance.
For example, if you ask, “What are the healthiest diets for over 70’s?” PaLM 2 can provide a balanced answer that takes into account various factors, such as age-related dietary needs, personal preferences, and the latest research on nutrition.
PaLM 2 excels at conversational AI, enabling users to interact with search results in a more human-like manner. Its ability to process and generate natural language text makes it ideal for delivering the sort of detailed, informative responses that SGE now provides.
OpenAI’s GPT-4
GPT-4, while not powering Google’s AI Overview, is another leading example of how generative AI is shaping the future of search. Like PaLM 2, it can generate detailed, accurate responses to a wide range of queries. Its strength, however, lies in its ability to predict the next word in a sequence, allowing it to produce coherent and contextually appropriate answers.
Although GPT-4 is often associated with chatbots like ChatGPT, its underlying technology is similar to what Google uses in AI Overview. These models are capable of producing not just short summaries but also more complex content, such as long-form answers or creative writing. In the search context, this could mean a more personalised and comprehensive user experience.
By using these advanced AI models, search engines like Google can move beyond just retrieving links to providing more human-like interactions. As these technologies continue to improve, we can expect even more personalised, accurate, and relevant search experiences. This will change not only how we search but also how businesses approach SEO.
What Is Google’s AI Overview?
A Summary of Google’s AI Overview
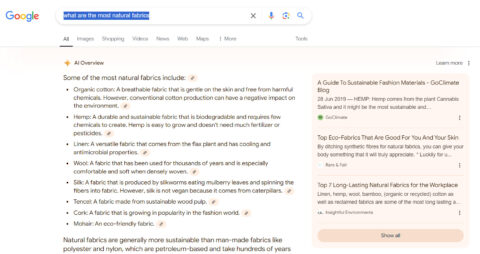
Google’s AI Overview, formerly known as SGE, is the company’s latest development in improving how users interact with search results. Launched in May 2024 in the U.S. and later expanded to all countries, including the UK, this AI-driven feature is designed to provide users with summarised answers directly in the search results. It allows for a more interactive and intuitive search experience by focusing on the user’s query intent, rather than just matching keywords.
Traditionally, Google search returned a list of relevant web pages based on ranking factors such as keywords, backlinks, and site authority. Users then had to manually browse these links to find the information they needed. AI Overview has changed all this by generating detailed, AI-driven summaries that are shown at the top of the search results page. These summaries are generated by LLMs that understand the context behind the query, drawing relevant insights from various sources across the web.
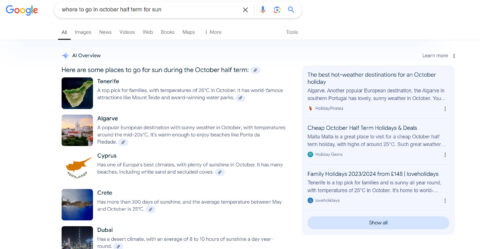
For example, if you search “where to go in October half term for some sun” AI Overviews would quickly generate a concise response such as: “Here are some places to go for sun during the October half term” and then list a number of options with links to click to get further information. This approach saves time and delivers a richer, more direct answer compared to traditional search processes where the user would need to explore multiple websites to gather this information.
Key Features of AI Overview
Google’s AI Overview offers several features that differentiate it from traditional search methods:
Summarised Answers
The core feature of AI Overviews is its ability to generate concise answers based on the user’s query. Rather than simply displaying a list of links, Google’s AI scans relevant documents, articles, and webpages to provide a summarised response without the user having to leave the Google interface.
Follow-up Questions and Interactive Suggestions
AI Overviews don’t just stop at providing a single answer; they encourage further exploration. After generating a summary, the AI presents follow-up questions to help users refine or expand on their query.
Dynamic and Context-Aware Responses
AI Overview adapts to the specific context of a search query. If a user submits a similar query with slightly different wording or searches multiple times in varying contexts, the AI will adjust its responses to reflect the nuances of the new search.
Links to Webpages for Further Reading
Although AI Overview provides quick, summarised answers, it also includes links to web pages for users who want to dive deeper into the subject. These links are often embedded directly within the AI Overview text.
How Can You Access AI Overview?
Unlike its earlier version (SGE), which was available only through Search Labs, AI Overview has now been rolled out to the general public in several regions, including the UK. You don’t need to sign up or enable any experimental features anymore. Just perform a search on Google, and if an AI Overview is available for your query, the summary will appear at the top of the results page.
Where is AI Overview Available?
As of July 2025, Google AI Overviews (formerly Search Generative Experience) are now globally available across over 200 countries and territories, supporting more than 40 languages.
How do I Opt Out of AI Overview?
If, as a website owner, you prefer not to have your content used in an AI Overview, you can opt out using methods like noindexing your page or utilising robots.txt. However, this action prevents your content from appearing in both the traditional search results and the AI generated summaries, so consider this carefully before implementing it.
It’s not something we’d recommend in many cases.
For those looking for a more measured approach, Google offers preview controls to limit the amount of content that can appear in search snippets or prevent snippets from being shown altogether. However, this approach might affect your site’s visibility, so it’s essential to weigh the pros and cons.
How Does Google’s AI Overview Work?
What’s The Technology Behind AI Overview?
Google’s AI Overview relies on several advanced technologies that work together to provide fast, relevant answers to user queries. These include natural language processing (NLP), machine learning (ML), and deep learning. While it may sound complex, these tools basically work behind the scenes to improve how we search and find information online.
At its core, NLP allows Google to understand the meaning and intent behind search queries. This means that instead of just matching keywords, Google can now grasp the context of a question. For instance, if you ask, “What are the best ways to reduce plastic in packaging?”, NLP helps the system understand that you are looking for methods to cut down on plastic use, not just information about plastic itself.
Once it understands the query, Google uses ML and deep learning to pull together relevant information from across the web. ML enables the search engine to learn from past searches and user interactions, continuously improving the results over time. Deep learning helps process the huge amounts of data involved, from websites to academic papers, news articles, and more. These technologies together allow Google to summarise key points and present useful information directly within the search results, rather than requiring users to click through multiple links.
An important feature of AI Overview is that the AI doesn’t just pull from one source; it gathers information from many, then summarises it in a way that’s easy to digest. You still get links to further reading, but the idea is to give you an instant, clear answer.
How are Large Language Models used in AI Overview?
Large Language Models (LLMs) are the backbone of Google’s AI Overview. One of the most significant models Google uses is PaLM 2, which is built to handle complex language tasks, including understanding nuanced questions, generating detailed responses, and even handling follow-up questions.
PaLM 2 is trained on a huge amount of text data, which gives it the ability to understand and respond to a wide variety of search queries. It can generate natural, conversational answers that go beyond basic keyword matching. This is important because people don’t always search using exact phrases. For example, a query like “best eco-friendly packaging alternatives” could mean you end up with a summarised answer that lists several options like biodegradable materials, reusable containers, and compostable plastics. These suggestions are based on its understanding of the query’s intent and the broad range of data it’s been trained on.
How does PaLM 2 Work?
- Query Understanding: PaLM 2 first breaks down the search query to understand the user’s intent. It does this by identifying key concepts and possible follow-up questions.
- Content Retrieval: The model then retrieves relevant documents from Google’s index, considering not just keywords but related topics and broader concepts.
- Summarisation: PaLM 2 takes all this information and pulls it into a concise summary. The goal is to provide a direct answer, often followed by links for more detailed exploration.
- Context-Awareness: If you continue interacting with the search results (e.g. asking follow-up questions), the AI adjusts and refines its answers based on what it has already provided, ensuring the responses stay relevant to the ongoing search.
Compared to Bing’s AI (which uses GPT-4), PaLM 2 provides a similar generative search experience, but Google emphasises the breadth of its knowledge base and the ability to pull from a wider range of sources. Bing, on the other hand, focuses more on conversational answers. Both systems use similar AI technology but have different approaches to structuring and presenting search results.
External Links for Further Reading:
- Learn more about Google’s use of AI in search.
- Details on Google’s PaLM 2 model and its impact.
What’s The Impact of Google’s AI Overview on SEO?
How is AI Overview Disrupting SEO?
Google’s AI Overview changes the way people search by giving them summarised answers directly in the search engine results page (SERP). Instead of clicking through multiple websites, users can get what they need in seconds.
This means:
- Less organic traffic to traditional websites
- A reduced need for users to visit multiple sources
- Potentially fewer opportunities for websites to monetise clicks
For businesses and SEO professionals, this represents a significant shift. Where once the aim was to rank on the first page of Google, it is now also crucial to ensure your brand and content are part of the knowledge base that AI Overviews draw upon.
What Are The Potential Challenges for SEOs?
- Reduced Click-Through Rates: If users get a satisfactory answer directly on the SERP, they are less likely to click through to your website.
- Loss of Control Over Messaging: AI may summarise your content in a way that does not align with your brand’s messaging or tone of voice.
- Increased Competition: Competing for citations or mentions within the AI Overview is the new battleground, which could prove difficult for newer or smaller sites.
- Risk of Hallucination: Generative AI may create incorrect or misleading summaries based on your content, potentially damaging trust.
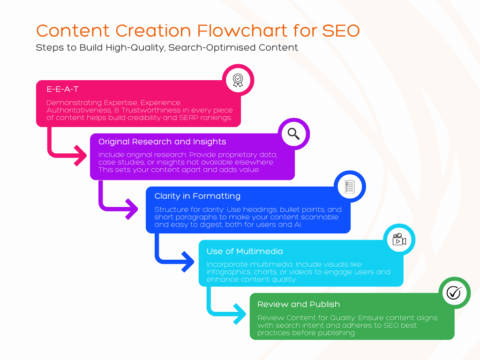
How to Optimise for AI Overviews
- Provide high-quality, authoritative content: Ensure your content is well-sourced, detailed, and trustworthy, so it is more likely to be cited in an AI summary.
- Use clear language: Write in a concise, accessible style to help AI models interpret and summarise your content accurately.
- Structure content logically: Use headings, bullet points, and other formatting tools to make your content easy to parse.
- Cover related questions: Anticipate follow-up questions a user might have and address them within your content.
- Leverage schema markup: Use structured data to help Google understand the context of your page, increasing your chance of being included in summaries.
How to Optimise Your Website for AI Overviews
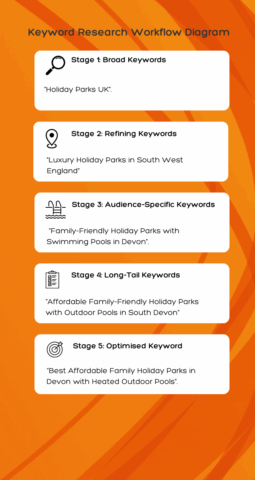
Long-Tail Keywords for AI Search
Traditional broad keywords may no longer be enough. Long-tail keywords are more likely to match nuanced, specific queries that AI can surface in its summaries. For example, instead of “business insurance,” try “affordable business insurance for UK freelancers.”
Create High-Quality, Unique Content
Generative AI depends on quality sources to build its answers. Content that is well-researched, data-driven, and unique has a far better chance of being summarised accurately.
Provide Unique Insights or Original Research
If you can offer original data, such as a new survey or research study, you increase the odds of being cited as a trusted source. AI systems love content that is not widely duplicated.
Use Clear and Concise Formatting
AI models prefer structured, clearly formatted information. This means:
- Short sentences
- Bullet points
- Numbered lists
- Clear section headings
This makes it easier for generative AI to extract meaningful summaries from your page.
Use Multimedia to Enhance Content
Rich media like charts, infographics, or videos can boost your Experience, Expertise, Authoritativeness and Trustworthiness (E-E-A-T) signals and help search engines see you as a high-value source.
How To Align Content With Search Intent
Aligning your content with search intent is crucial in optimising for AI Overviews. Google’s AI is designed to provide the most relevant and useful information for a given query, so your content must directly answer the user’s underlying intent behind their search.
Users typically search with one of the following intents:

Informational: Seeking knowledge or answers to a question (e.g.”how to create a website”).

Navigational: Looking for a specific website or page (e.g.”Koozai Digital Marketing”).

Transactional: Ready to make a purchase or complete a task (e.g.”book a Koozai SEO audit”).

Commercial: Researching products or services before making a purchase
decision (e.g.”Costs of Koozai SEO audits”).
Understand what users really want. If someone searches “how to start a small business in the UK” they probably want practical, step-by-step information, not a 2000-word essay. Align your content to answer those needs directly.
Use Schema Markup
Structured data is a powerful tool for helping AI engines understand your website’s content. Adding schema markup allows you to provide context about your content, making it easier for Google’s AI to accurately summarise and present your information in AI Overviews.
Importance of Structured Data
- Enhances Content Discovery: When you implement structured data, you make it easier for search engines to index your content
effectively. This can lead to better visibility in search results and increase the likelihood of being featured in AI summaries. - Improves Click-Through Rates: Pages with structured data often display rich snippets in search results, which can enhance their appearance and attract more clicks. For instance, a holiday park page with structured data about amenities might show up with star ratings, operational hours, or even images, which can entice users to click.
- Helps Google Match Content with User Intent: Using schema markup, such as FAQ schema or how-to schema, helps Google understand the type of content on your page and match it with relevant user queries. For example, adding FAQ schema to a blog post about holiday park activities can ensure that specific questions like “What activities are available at [Holiday Park Name]?” are highlighted in search results.
Types of Schema to Consider
- Local Business Schema: Ensure to implement local business schema to provide Google with your address, contact information, and operating hours, which can improve local search visibility.
- FAQ Schema: For example use this for content that addresses common questions related to holiday parks or services. This can boost your chances of appearing in voice search results or AI Overviews.
- How-To Schema: This is beneficial for guides, such as “How to Plan a Family Trip to a Holiday Park.” By using this schema, you can increase the likelihood that your content is featured in SGE responses.
There are many types of schema; these are just a few examples. Look into all those that would be relevant to your business.
Continually Update and Refine Content
Search intent can change over time, especially in industries that are fast moving. Regularly review and update your content to ensure it remains aligned with the current intent behind target keywords. This is particularly important for evergreen content, which needs to stay relevant to continue ranking.
Answer Related Questions
Including related questions and answers within your content is an effective way to boost your chances of being featured in AI Overviews. This approach, often referred to as People Also Ask (PAA) optimisation, helps Google understand that your content is comprehensive and addresses the various angles of a topic.
How to optimise content by answering related questions:
- Structure content to reflect multiple angles: Make sure that your content is structured in a way that addresses different aspects of the main topic. For example, in an article on “best project management tools,” you could have separate sections discussing tools for small teams, remote work, and industry-specific needs like construction or software development.
- Identify common related questions: Tools like AnswerThePublic, AlsoAsked, or Google’s own “People Also Ask” boxes can help you discover the kinds of related questions users might have. For example, if you’re optimising content about “best CRM software for small businesses,” you might find related questions like “Is HubSpot good for small businesses?” or “What is the easiest CRM to use?”
- Incorporate FAQ sections: Adding an FAQ section at the end of your blog post or guide can be a simple way to address related questions. Ensure each question is followed by a clear, concise answer that directly addresses the query. For example, in a guide on CRM tools, you could include questions like “What CRM is best for startups?” and “How do I choose the right CRM for my business?”
- Provide direct and concise answers: When answering related questions, it’s important to be as clear and direct as possible. Google’s AI values content that gets straight to the point and provides actionable insights. Avoid overly long or complex answers
Build Authoritative Links
Backlinks from authoritative sites remain one of the strongest signals to Google that your content is valuable and trustworthy. Earning high-quality links not only improves your organic ranking but also increases the likelihood that your content will be selected for AI Overviews.
Steps to build authoritative links:
- Create linkable assets: Focus on developing content that other businesses and websites will want to reference or link to. This could include comprehensive guides, original research, or valuable tools. For example, a digital marketing agency specialising in hospitality could
create a “Guide to Eco-Friendly Practices for Holiday Parks.” This guide could cover sustainable accommodation options, eco-friendly guest amenities, and renewable energy solutions. By providing actionable tips and showcasing case studies, it becomes a valuable resource that attracts backlinks from industry blogs, environmental organisations, and hospitality news outlets. - Engage in digital PR: Public relations strategies, such as pitching stories to journalists, contributing articles, or collaborating on industry reports, can help you earn links from high authority domains. These backlinks signal to Google that your content is reputable, increasing the chances of it being featured in AI Overviews.
- Monitor competitors’ backlinks: Use tools like Ahrefs or Moz to analyse where your competitors are earning links. This can help you identify potential backlink opportunities for your own content.
- Focus on relevance: While quantity is important, the relevance of your backlinks is even more crucial. Links from authoritative sites within your industry carry more weight than general links from unrelated sources.
While Google’s AI Overviews are changing how users engage with search results, the fundamental principles of SEO remain. By focusing on high-quality, intent-driven content and optimising for niche queries, you can continue to improve. Though traffic patterns may shift, SEO is far from dead, it’s simply adapting to a new reality
How to Measure the Impact of SGE on Your SEO Strategy
As SGE reshapes the way users interact with search results, it’s crucial to measure how these changes affect your SEO strategy. This section will guide you through the tools and techniques you can use to track the performance of AI-generated search results and how to optimise conversions from the traffic driven by SGE/AI Overviews.
Tracking SEO Performance for SGE
When it comes to SGE, traditional SEO metrics still matter, but the way you track and interpret them may need to change. As AI generated overviews increasingly dominate search, understanding how your content performs within these results is key to maintaining visibility.
Key Tools and Metrics
- Keyword Tracking for AI-Driven Results: Traditional keyword tracking tools like SEMrush, Ahrefs, and Google Search Console still play a crucial role in monitoring your rankings. However, you now need to focus on tracking where your content appears in AI-generated responses as well as its visibility in standard search results.
- Tracking Long-Tail Keywords: Since SGE often addresses broad queries directly in the AI overview, long-tail keywords remain a valuable area of focus. For example, a query like “best remote work tools for small businesses” might trigger a direct AI-generated response, summarising top software options. Your goal is to identify niche, long-tail keywords that drive traffic to your website, beyond what the AI generates.
- SERP Features: Pay close attention to new search features linked to AI-generated results. These include AI-powered summaries, People Also Ask boxes, and related searches, all of which can affect how much organic traffic your site gets. Use tools like Ahrefs to track whether your content appears in these enhanced features.
- Analysing Click-Through Rates (CTR): CTR is a key indicator of how users interact with your content after viewing an AI-generated response. When your page appears as a source in an AI summary, the summary often includes a link to your website. Keep a close eye on how these AI-driven links affect your overall CTR compared to traditional search results.
- A/B Testing Meta Descriptions: To improve your CTR, test variations of meta descriptions and headlines. For instance, if users search for “best eco-friendly coffee shops in Southsea,” you might A/B test whether a meta description like “Explore Southsea’s Top Sustainable Cafes” leads to higher engagement compared to something more generic.
- Page Impressions and Traffic Volumes: While traffic from traditional organic search might fluctuate as SGE becomes more prominent, it’s essential to track how much of your site’s overall traffic is driven by AI-generated search summaries. Google Search Console can help you track impressions and clicks from search, while Google Analytics shows how much traffic comes from search versus other channels.
- Search Traffic Segmentation: In your analytics tool, create segments to differentiate between traffic coming from AI-driven results and traditional search. This will help you see how well your content is performing across both types of search experiences
TIP: Let’s say your website offers remote work solutions. A query like “best tools for remote teams” might generate an AI summary listing popular solutions. Use Google Analytics to monitor whether users clicking on your link within that AI overview are staying longer on your site, bouncing quickly, or converting into leads.
Conversion Optimisation for SGE Traffic
Once you’ve attracted visitors through AI-generated results, the next challenge is to optimise those conversions. Traffic from AI summaries may behave differently from traditional search users, as they often arrive at your site with some prior knowledge gained from the overview.
- Aligning Landing Pages with AI-Generated Content: SGE often provides users with a broad summary before they click on a specific link. To optimise your conversions, make sure your landing page reinforces and expands on the information already provided in the AI summary.
- Address Pre-Qualified User Expectations: Users arriving from AI-generated search results are typically pre-qualified. They’ve already been exposed to part of your content via the AI overview. To improve conversions, make sure your landing pages cater to what users already know, avoiding unnecessary repetition of the information they’ve seen in the AI response.
For example: If the AI-generated result for “top stargazing locations on the Isle of Wight” lists your site as a source for one of the best stargazing spots, your landing page should not just restate that. Instead, it could provide additional details such as the best times of year for stargazing, what facilities are available, and any nearby accommodation options. This provides more value to the user and encourages further engagement, whether through newsletter signups or bookings.
- Create Content that Complements AI Summaries: Rather than focusing only on what the AI might summarise, consider creating content that complements it. For instance, if the AI summary covers broad points, use your landing page to dive deeper into niche details or offer related services or products.
For example: A blog post titled “How to Choose the Best Eco-Friendly Cleaning Products” might be summarised in an AI overview. If users click through to your page, make sure your landing page goes beyond the basics by offering detailed product comparisons, eco-certifications, and case studies about environmental impact. This adds more depth than the AI summary and increases the likelihood of conversions
Measuring User Behaviour and Adjusting for AI Traffic
Finally, it’s important to continually monitor and adjust based on how AI-driven traffic behaves on your site. Since AI-generated results tend to summarise content, users may come to your site with more specific questions or needs than traditional search visitors.
Key Behaviour Metrics to Track
- Bounce Rate and Time on Page: If visitors arrive on your page after reading an AI summary, they might be looking for specific information. A high bounce rate could indicate that your landing page doesn’t meet their expectations, or it simply repeats information already covered by the AI overview. On the other hand, longer time on page may suggest that your content is successfully engaging visitors beyond the initial AI summary.
- Scroll Depth: Monitor how far users scroll down your pages. If users from AI-generated search results are leaving after reading the first few sentences, it may indicate that your content doesn’t provide enough additional value. By adjusting your content layout or adding more interactive elements (such as videos or FAQs), you can encourage visitors to engage further.
- Conversion Rate: Track how AI-driven traffic converts compared to visitors from traditional search results. If you notice that AI-driven traffic converts at a lower rate, consider A/B testing different landing page elements or adjusting the content to better meet user expectations.
- Continual Optimisation: SGE and AI search will continue to change, so your strategy should be flexible. Regularly review the performance of AI-generated traffic, experiment with different approaches, and adapt your content and conversion paths as needed.
Measuring the impact of SGE on your SEO strategy requires a mix of traditional SEO performance metrics and new approaches to cater to AI-driven search experiences. By focusing on keyword tracking, user behaviour, and conversion optimisation, you can ensure that your website remains competitive as AI search becomes more prominent.
Comparing Google AI Overview with Other AI-Powered Search Engines
Understanding the differences between these technologies will help you use each platform effectively within your SEO strategy and optimise content for different search experiences.
Google AI Overview vs. ChatGPT
Google’s AI Overview and OpenAI’s ChatGPT both use AI to deliver conversational search experiences, but their approaches and use cases vary significantly. While both tools focus on generating relevant information, they are designed for different purposes, and users typically engage with them in different ways.
How They Work
Google’s AI Overview: Google’s AI Overview is integrated directly into Google Search, providing users with AI-generated
summaries on search engine result pages (SERPs). It focuses on blending traditional search with AI-powered overviews, helping
users quickly gather key insights from multiple sources. The AI-generated responses are embedded within Google’s established
ranking systems, pulling information from a wide range of content on the web.
ChatGPT: ChatGPT, developed by OpenAI, is designed as a conversational AI model. It excels in responding to complex queries
in a chat-like format, offering more direct, dialogue-based interaction. ChatGPT is not a search engine in the traditional sense, it
doesn’t pull live data from the web in real time (unless using a browser plugin) but instead uses the vast amount of information it
was trained on to provide answers.
Use Cases
Product Research and Comparison: Google’s AI Overview is more efficient for product research that requires up-to-date
information or comparison of multiple items. For instance, if a user searches “best remote work software for small businesses,” AI
Overview will pull information from various online sources, offering a concise yet multi-perspective overview. This is particularly
useful when users want recent product reviews or a quick summary from various trusted websites.
On the other hand, ChatGPT excels when users want a more in-depth, explanatory type response. If someone asks ChatGPT,
“What features should I consider when choosing remote work software?” the tool will generate a comprehensive, conversational
response that explains key considerations in greater detail, but it may not always reference the most up-to-date tools or reviews
unless connected to a live browsing feature.
- Google AI Overview: Best for quick summaries of current topics
- ChatGPT: Best for deep explorations, explanations, or brainstorming
Strengths and Limitations
Google’s AI Overview: Its main strength lies in how seamlessly it integrates with live data, making it ideal for searches that
require current information or insights from a variety of sources. However, the answers are generally brief, and users may need to
click through to actual web pages for in-depth content.
ChatGPT: The conversational nature of ChatGPT makes it excellent for generating long-form content or assisting with creative
tasks like drafting blog posts or brainstorming ideas. However, because it isn’t constantly pulling live data from the web, ChatGPT
can sometimes present outdated information if not used in conjunction with live plugins.
Google’s AI Overview vs. Bing AI
Microsoft’s Bing AI has also integrated artificial intelligence into its search engine, creating a strong competitor to Google’s AI
Overview. Both offer AI-enhanced results, but there are key differences in how these platforms operate and what they offer to
users.
How They Work
Google AI Overview: Google is primarily focused on integrating AI into its search results, offering concise, AI-generated answers alongside traditional organic listings. It gathers data from across the web, presenting users with summarised information directly on the SERP without requiring them to navigate through multiple websites.
Bing AI: Bing’s AI integrates OpenAI’s GPT technology, similar to ChatGPT, but with the added ability to browse live web data, thus offering a more dynamic approach. Bing AI offers both conversational responses and standard search results. Its chat-based interface allows users to ask follow-up questions, encouraging a more interactive, detailed search experience. For instance, if a user asks about “best productivity tools for developers,” Bing AI can not only list the top tools but also provide links to reviews, pricing, and other real-time details.
Use Cases
Complex Search Queries: Bing AI is particularly strong when handling complex or multi-part queries. For example, if someone searches for “best productivity tools for developers,” Bing AI’s ability to respond in a conversational way means it can follow up with additional questions like “What’s your budget?” or “Do you need open-source tools?” This interactive search approach helps users refine their queries for more personalised results.
Google’s AI Overview, on the other hand, is optimised for users who prefer quick, summarised answers. The AI-generated response for “best productivity tools for developers” in Google would likely provide a succinct overview of the most popular tools, with links to external sources for further reading. This makes it efficient for users who want fast answers without diving too deep into specifics.
- Bing AI is also built on generative language models (GPT-4), blended with its traditional search
- Offers a more conversational experience than Google
- More interactive with follow-up questions
- Similar to Google AI Overview, Bing places generative answers directly within the search results
Key Differences
Interface:
- Google AI Overview is embedded within the familiar Google Search interface, making it ideal for users who want a streamlined experience without leaving the SERP. Users get both traditional results and AI-powered overviews in a single view.
- Bing AI while also offering traditional search results, places greater emphasis on its conversational interface. Users can interact with the AI to refine their queries or explore topics in greater detail through a chat-like experience.
Personalisation and Interactivity:
- Bing AI tends to be more interactive, allowing users to ask follow-up questions directly within the search session. This is particularly helpful for complex searches where additional context or clarification is required.
- Google AI Overview, while efficient at presenting overviews, and offering some follow-up questions, doesn’t yet have the same level of interaction. Users will need to retype their questions or start new searches to refine the information provided.
Depth vs. Brevity:
- Bing AI often provides more in-depth responses thanks to its integration with GPT-based technology. For users who need detailed information or explanations, Bing AI excels at offering nuanced answers.
- Google AI Overview focuses on brevity, offering high-level summaries that are helpful for users in a hurry or those looking for quick comparisons. The responses in AI Overviews are more concise, often encouraging users to visit external sites for further details.
Key Similarities
Despite these differences, Google AI Overview and Bing AI share several commonalities. Both are focused on improving search efficiency and delivering more personalised, AI-driven results.
- AI Summarisation: Both platforms utilise AI to generate summaries based on user queries, making search results more accessible and faster to digest.
- Improved User Experience: Both Google and Bing are investing in making search results more intuitive. Whether through summarised overviews or interactive chat, the end goal is to help users find relevant information more quickly.
- Integration with Traditional Search: Neither Google SGE nor Bing AI has completely replaced traditional search listings. In both systems, AI-generated responses are an enhancement rather than a full substitute, with standard organic search results still playing a critical role.
When comparing Google’s AI Overview with OpenAI’s ChatGPT and Bing AI, it’s clear that while all three platforms rely on AI to improve search and information retrieval, they serve different user needs. Google excels at delivering quick, AI-enhanced overviews within the familiar search environment, making it perfect for users seeking concise answers and up-to-date information.
ChatGPT, by contrast, is best suited for generating detailed, conversational content, while Bing AI’s blend of search and conversational AI offers an interactive experience that’s ideal for complex or follow-up queries.
For SEOs and content creators, understanding these differences is key to optimising your strategy. By aligning your content with the strengths of each platform, you can ensure that your website remains visible and relevant.
The Future of AI in Search and SEO
AI’s influence on search and SEO is accelerating rapidly, driven by innovations like Google’s Gemini model and Bing’s generative search. These advancements mark the beginning of a broader shift toward more personalised, multimodal, and intelligent search experiences. This chapter explores key AI trends reshaping search and SEO, along with practical insights on how businesses and SEOs can stay competitive.
Emerging AI Trends in Search
Artificial intelligence is revolutionising how we search for information, with new capabilities enhancing personalised, visual, and conversational search experiences. Understanding these trends is critical for anyone involved in SEO or digital marketing.
Personalised Search Experiences
AI is enabling search engines to deliver highly personalised results, driven by ML and huge data insights. Google’s Gemini model, for instance, enhances search by understanding user preferences, behaviours, and even context to tailor results. Personalisation will continue to develop in key areas:
- User intent: AI is improving its ability to interpret vague or imprecise queries, and Google’s AI Overviews now provide summaries with direct links to sources for further exploration. This shift emphasises the importance of content optimised for diverse user intents.
- Behaviour patterns: Search engines are using personal data, like browsing history and location, to provide customised results. Google is now using AI to organise search results pages by relevance, making it easier to discover content from various sources.
This level of personalisation raises the bar for content optimisation. Businesses must ensure they create value-driven content tailored to different audience segments, with a stronger focus on context and intent
The Growth of Conversational Commerce
AI-powered search is moving beyond information retrieval to enable seamless transactions, paving the way for conversational commerce. With the integration of tools like Google Lens and voice search, users can now ask questions with their voice or camera and receive relevant AI-driven results, often linked to shopping options.
- Generative AI Overviews: In the US Google has incorporated ads into AI Overviews, helping users discover relevant products and services at the exact moment they need them. And it likely won’t be long before we see these here in the UK too. For instance, someone searching for ways to remove grass stains might see product ads embedded within AI responses, streamlining the purchasing process. SEO professionals need to optimise content for AI-driven transactional searches, emphasising conversion-oriented experiences. Structured data and schema markup will continue to play a key role in helping search engines interpret content for transactional queries.
- Voice and Multimodal Search: Advances in AI are also enhancing voice and multimodal search capabilities, allowing users to search via images, videos, or voice commands. Google Lens, which now processes nearly 20 billion visual searches monthly, is a prime example. Users can snap a picture or take a video and ask questions like, “Where can I buy this?” or “What type of fish is this?”. Video understanding in Google Lens now allows users to record a video and ask questions about moving objects, receiving AI generated insights in real-time. This technology is transforming how people engage with search, particularly among younger audiences.
SEOs must adapt to this by optimising content for various input types, ensuring that visual, voice, and video queries are considered in the content strategy. Optimising images, metadata, and multimedia elements becomes even more essential.
AI-Assisted Content Creation
AI is also playing a big role in content creation, making it easier for businesses to generate relevant, high-quality content. AI-driven tools can help with keyword research, content planning, and writing, improving efficiency without sacrificing quality. Tools like Google’s Gemini and Bing’s Generative Search deliver more in-depth responses, offering users expanded insights for complex or research-heavy queries.
While AI tools are streamlining content creation, SEO professionals must still focus on strategic planning and crafting unique, value-rich content that aligns with the user’s intent.
Preparing for the Next Phase of SEO
The future of SEO lies in being able to adapt to the impact these changes are having. Here are some practical steps to ensure your website remains competitive:
- Focus on High-Value Searches
As search engines become more personalised, targeting high-value searches, those with clear intent and high conversion potential, will be crucial. For instance, optimising for specific, intent-driven queries like “eco-friendly backpacks for students” can drive more qualified traffic than broad terms like “backpacks.” - Continuous Content Optimisation
With AI now organising search results dynamically, content relevancy is assessed in real time. SEOs and businesses must continuously update and optimise content based on user needs, staying responsive to shifting trends. Tools like Google Lens and AI Overviews make it easier for users to find the most up-to-date information, further emphasising the need for regular content updates. - Use AI-Based SEO Tools
AI-based SEO tools can assist with everything from keyword research to competitor analysis and real-time content optimisation. Platforms like Google’s Lens, SEMrush, and SurferSEO provide insights into how content aligns with AI-powered search algorithms, making it easier to stay ahead of trends. - Embrace Schema Markup
Schema markup is essential for helping AI-driven search engines understand and present content. With AI-powered tools like Lens making it easier to shop visually, using structured data to mark up reviews, product details, and availability will be key for appearing in featured snippets and AI-generated summaries. - Enhance User Experience (UX)
User experience is a growing priority for AI-powered search. Sites that are fast, mobile-responsive, and easy to navigate will rank higher in search results. Google’s focus on AI-organised search results pages further highlights the importance of UX in ensuring visitors engage with and convert on your site.
To stay competitive, SEOs must engage with AI-driven tools, optimise for a range of search inputs, and focus on creating high quality, conversion-oriented experiences. By staying ahead of these trends, businesses can continue to be successful online.
In summary:
- Optimise for high-intent, high-value keywords
- Keep your content fresh
- Improve E-E-A-T signals
- Invest in building authoritative links
- Ensure your technical SEO supports fast, structured, accessible content
- Align your PR, content, and SEO efforts to become a cited brand
Conclusion
We hope you’ve found this long form blog useful. It’s clear that search engine optimisation is undergoing significant change due to the rise of AI, particularly through Google’s AI Overview. As AI becomes even more central to search engines, businesses and marketers need to rethink how they approach SEO to maintain visibility.
This blog has explored how AI models like Google’s PaLM 2 and OpenAI’s GPT-4 are changing the way search results are delivered. AI’s ability to understand context and provide direct answers impacts traditional SEO strategies. With Google’s AI Overview generating summaries directly on search results pages, websites may see fewer clicks, which means standard metrics like click-through rates are no longer the only measures of success.
To stay competitive, businesses should focus on adapting their SEO strategies. This includes optimising for long-tail keywords, aligning content with user intent, and creating unique, high-quality content that AI can use in its summaries. We’ve seen that using structured data, building authoritative links, and continuously updating content are also key.
As AI technology continues to develop, businesses must stay proactive. Embracing AI-based SEO tools and continuously refining content will help ensure long-term success. The future of SEO lies in understanding and adapting to the changes.
Take action now to adjust your SEO strategy for AI. Ensure your content is optimised, your site is structured to support AI-driven searches, and your digital marketing approach is aligned with this new reality. Staying ahead of the curve will help your business maintain visibility and drive meaningful results. Please feel free to contact us if you need help with any of this.






Leave a Reply